The EN 1779 norm - Leak detection method clasification
The basic functions of leak detection are the location and measurement of leaks. These functions are carried out through the use of standard leak test techniques, which are usually selected according to the configuration ofthe part to be tested, the economics of the test, and the nature of the system. It is recommended to maintain the same conditions as when the tested product is being used, e.g. the same pressure level and gas flow. For examples, a vacuum system should be tested in a vacuum chamber where as compressed-air bottles should be tested under high pressure.
Leak Location
Leak location is the testing approach used to find the precise location of individual leaks. It is usually a qualitative procedure only. Leak location does carry out the very valuable function of identifying the sources of measured leaks in order to facilitate repair, remanufacture, or, in some cases, even redesign.
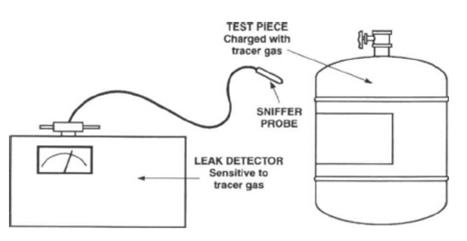
Leak location is carried out by means of two techniques, termed the snifferprobe mode and the spray-probe mode.
In the sniffer-probe mode, the test piece is filled with tracer gas and the exterior is scanned with a probe that is attached to the inlet of the leak detector. The probe continuously admits (or "sniffs") some of the air directly surrounding the test piece. This air is inducted to the analytical portion of the leak detector, where any of the tracer gas that may be leaking from the test piece is detected.
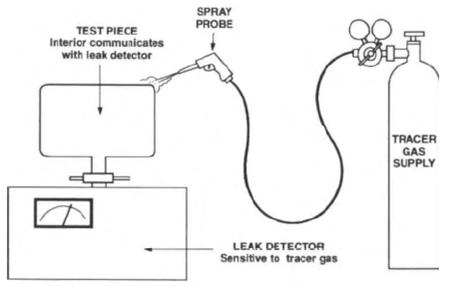
In the spray-probe mode, the leak detector is used to evacuate the interior of the test piece, and a probe is used to discretely spray test gas on suspected leak sites. Any leaks are evidenced when the tracer gas flows through
the evacuated test piece and is detected by the leak detector.
Leak Measurement
Leak measurement is the approach used to actually measure the total or partial leakage of a device or system. The most reliable approach is to initially test a system or device for total leakage, and then for individual leaks, which are isolated by using one of the leak location techniques. Use of a leak location technique to measure total leakage usually results in poor reliability and high cost.
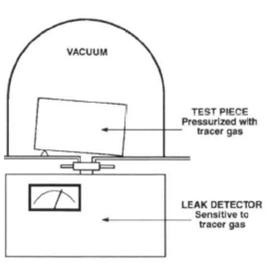
The two standard leak measurement techniques are known as the inside-out mode and the outside-in mode. In the inside-out mode, the test part is filled with tracer gas and is placed in a test fixture that is subsequently evacuated. Any of the tracer gas that flows out through a leak is captured in a volume surrounding the test part. The contents
of this volume are analyzed by the leak detector as representative of total leakage.
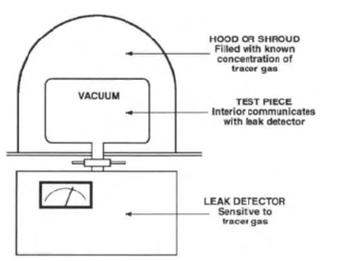
In the outside-in mode, the test part is evacuated and is placed in a volume containing the tracer gas, which flows through all leaks to the interior of the test part, where it is detected.
With either of these approaches, the tracer gas may be allowed to accumulate before detection, or may be detected continuously. In general, continuous detection yields a faster test with adequate sensitivity; however, circumstances
sometimes require the accumulation of tracer gas prior to analysis.






